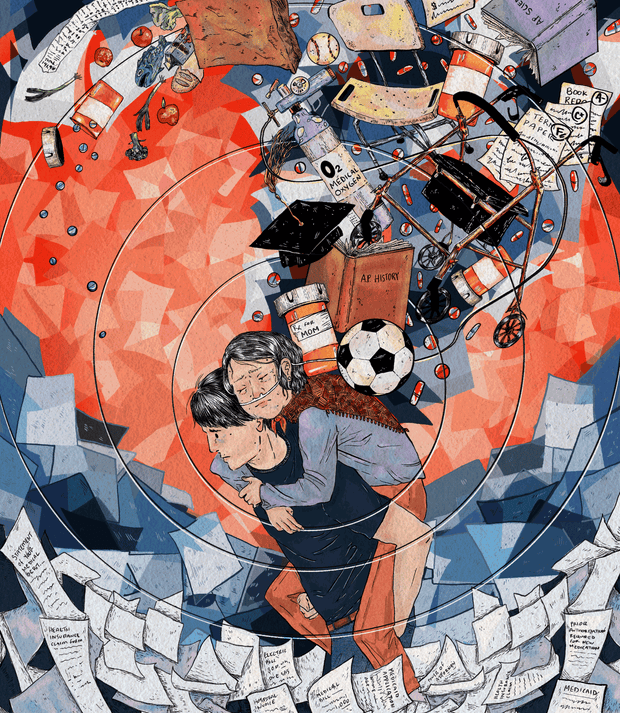
ST. PAUL, Minn. — High school senior Joshua Yang understands sacrifice. When he was midway through 10th grade, his mom survived a terrible car crash. But her body developed tremors, and she lost mobility. After countless appointments, doctors diagnosed her with Parkinson’s disease, saying it was likely triggered by brain injuries sustained in the wreck.
At 15, Yang, an aspiring baseball player and member of his school’s debate team, took on a new role: his mother’s caregiver.
Researchers estimate that Yang, now 18, counted among at least 5.4 million U.S. children who provide care to an adult in their home. As state officials eye federal Medicaid funding cuts that could drastically reduce home care services for those who are disabled or have chronic health conditions, many predict that number will rise.
That’s bad news for kids: Studies show that when young people take on care for adults with medical conditions, their health and academic outcomes decline. At the same time, their loved ones receive untrained care.
“It all fell to me,” said Yang, whose sisters were 9 and 10 at the time of their mom’s accident, and whose stepdad worked nights. His grades fell and he quit after-school activities, he said, unable to spare the time.
Early on, Yang found reprieve from a personal care nurse who gave them supplies, such as adult diapers, and advice on items to purchase, such as a chair for the shower. And for about a year, Yang was able to work for a personal care agency and earn $1,000 a month caring for his mom — money that went toward her medication and family needs.
But at the beginning of 11th grade, a change to his mom’s insurance ended her personal care benefit, sending him into a runaround with his county’s Medicaid office in Minnesota. “For a solid month I was on my phone, on hold, in the back of the class, waiting for the ‘hello,'” he said. “I’d be in third period, saying, ‘Mr. Stepan, can I step out?'”
A report published in May by the U.S. Government Accountability Office reminded states that National Family Caregiver Support Program grants can be used to assist caregivers under 18. However, the future of those grants remains unclear: They are funded through the Older Americans Act, which is awaiting reauthorization; and the Administration for Community Living, which oversees the grants, was nearly halved in April as part of the reorganization of the Department of Health and Human Services under President Trump.
Additionally, if Congress approves proposed cuts to Medicaid, one of the first casualties likely will be states’ home- and community-based service programs that provide critical financial relief to family caregivers, said Andrew Olenski, an economist at Lehigh University specializing in long-term health care.
Such programs, which differ by state but are paid for with federal dollars, are designed to ensure that Medicaid-eligible people in need of long-term care can continue living at home by covering in-home personal and nursing care. In 2021, they served almost 5% of all Medicaid participants, costing about $158 billion.
By law, Medicaid is required to cover necessary long-term care in a nursing home setting but not all home or community care programs. So, if states are forced to make cuts, those programs are vulnerable to being scaled back or eliminated.
If an aide who makes daily home visits, for example, is no longer an option, family caregivers could step in, Olenski said. But he pointed out that not all patients have adult children to care for them, and not all adult children can afford to step away from the workforce. And that could put more pressure on any kids at home.
“These things tend to roll downhill,” Olenski said.
Some studies show benefits to young people who step into caregiving roles, such as more self-confidence and improved family relationships. Yang said he feels more on top of things than his peers: “I have friends worrying about how to land a job interview, while I’ve already applied to seven or eight other jobs.”
But for many, the cost is steep. Young caregivers report more depression, anxiety, and stress than their peers. Their physical health tends to be worse, too, related to diet and lack of attention to their own care. And caregiving often becomes a significant drag on their education: A large study found that 15- to 18-year-old caregivers spent, on average, 42 fewer minutes per day on educational activities and 31 fewer minutes in class than their peers.
Schools in several states are taking notice. In Colorado, a statewide survey recently included its first question about caregiving and found that more than 12% of high schoolers provide care for someone in their home who is chronically ill, elderly, or disabled.
Rhode Island’s education department now requires every middle and high school to craft a policy to support caregiving students after a study published in 2023 found 29% of middle and high school students report caring for a younger or older family member for part of the day, and 7% said the role takes up most of their day. Rates were higher for Hispanic, Asian, and Black students than their white peers.
The results floored Lindsey Tavares, principal of Apprenticeship Exploration School, a charter high school in Cranston. Just under half her students identified as caregivers, she said. That awareness has changed conversations when students’ grades slip or the kids stop showing up on time or at all.
“We know now that this is a question we should be asking directly,” she said.
Students have shared stories of staying home to care for an ill sibling when a parent needs to work, missing school to translate doctors’ appointments, or working nights to pitch in financially, she said. Tavares and her team see it as their job to find an approach to help students persist. That might look like connecting the student to resources outside the school, offering mental health support, or working with a teacher to keep a student caught up.
“We can’t always solve their problem,” Tavares said. “But we can be really realistic about how we can get that student to finish high school.”
Rhode Island officials believe their state is the first to officially support caregiving students — work they’re doing in partnership with the Florida-based American Association for Caregiving Youth. In 2006, the association formed the Caregiving Youth Project, which works with schools to provide eligible students with peer group support, medical care training, overnight summer camp, and specialists tuned in to each student’s specific needs. This school year, more than 700 middle and high school students took part.
“For kids, it’s important for them to know they’re not alone,” said Julia Belkowitz, a pediatrician and an associate professor at the University of Miami who has studied student caregivers. “And for the rest of us, it’s important, as we consider policies, to know who’s really doing this work.”
In St. Paul, Joshua Yang had hoped to study civil engineering at the University of Minnesota, but decided instead to attend community college in the fall, where his schedule will make it simpler to continue living at home and caring for his mom.
But he sees some respite on the horizon as his sisters, now 12 and 13, prepare to take on a greater share of the caregiving. They’re “actual people” now with personalities and a sense of responsibility, he said with a laugh.
“It’s like, we all know that we’re the most meaningful people in our mom’s life, so let’s all help out,” he said.
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.